تطور تطبيقات التعلم التعزيزي العميق في الروبوتات الذكية: دليلك الشامل
مقدمة
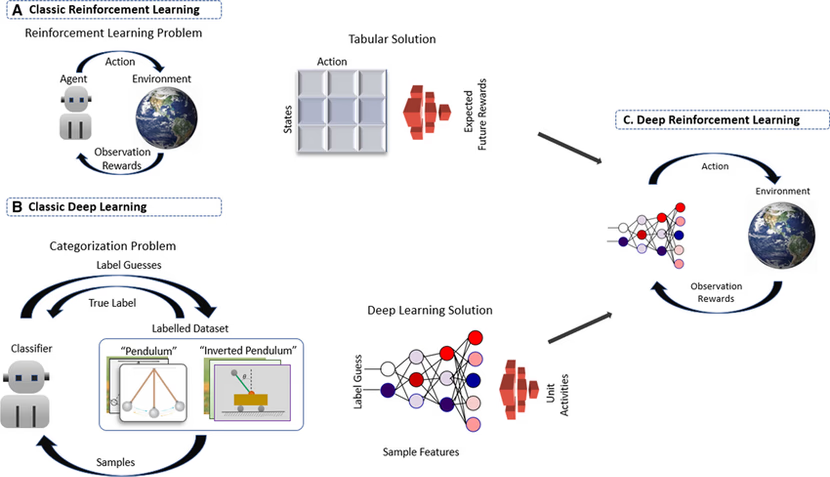
في العقدين الماضيين، شكّل التعلم التعزيزي حجر الزاوية للذكاء الاصطناعي القادر على التعلم من التجربة. ومع اندماج تقنيات التعلم العميق (Deep Learning) لتمثيل المدخلات الحسّية المعقدة، ظهر مجال التعلم التعزيزي العميق (DRL)، الذي مكن الوكلاء (Agents) من التحرك ضمن فضاءات حالة ضخمة وغير مهيكلة (صور، صوت، بيانات حسية). في المقابل، كانت البرمجة التقليدية تفتقد المرونة المطلوبة للتكيف مع بيئات ديناميكية متغيرة باستمرار.
في هذا المقال الموسع (1500 كلمة)، نسترعي الانتباه إلى:
- الأساس النظري والتاريخي لـ DRL.
- مكونات وآلية عمله مفصلة.
- أهم الخوارزميات وتطوراتها (2023–2025).
- تطبيقات عملية في روبوتات Boston Dynamics وغيرها.
- التحديات التقنية والحلول.
- التوجهات المستقبلية حتى عام 2030.
المراجع
Deep reinforcement learning (deep RL) | EBSCO
Deep reinforcement learning (deep RL) is an advanced approach to training artificial intelligence (AI) that merges reinforcement learning with deep learning techniques. In reinforcement learning, AI systems learn to make decisions by exploring different actions within an environment, gradually refining their strategies based on rewards received for achieving specific goals. Deep RL enhances this process by incorporating deep neural networks with multiple layers, enabling the AI to efficiently analyze vast datasets and recognize complex patterns. This method has led to significant breakthroughs in various domains, particularly in games where deep RL algorithms, such as AlphaGo, have outperformed top human players in complex board games and video games. While deep RL offers promising capabilities, it also raises concerns about job displacement and ethical implications, as its increasing efficiency could lead to significant changes in the workforce. Proponents believe that, if developed responsibly, AI could enhance human productivity and open new avenues for scientific advancement, potentially leading to a more automated and efficient society. Overall, deep RL represents a significant evolution in AI, combining the strengths of learning from both large datasets and strategic decision-making.
تصفح المرجع1. ماهية التعلم التعزيزي العميق وأهميته في الروبوتات الذكية
1.1 من البرمجة التقليدية إلى التعلم التعزيزي
•البرمجة التقليدية: تتطلب هندسة خصائص يدوية لكل سيناريو، ما يجعل التوسع والتكيف عملية مكلفة ومعقدة.
•التعلم التعزيزي (RL): يتيح لوكيل التعلم عبر المكافآت والعقوبات، مما يقلل الحاجة للقواعد الصارمة.
•التعلم العميق (DL): اعتمد على الشبكات العصبية لاستخلاص تمثيلات بيانات عالي الأبعاد (كصور الكاميرا أو بيانات الليدار).
1.2 تعريف DRLDeep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) هو تكامل بين مبدأي RL وDL:
•شبكات عصبية عميقة كمقرّبات دوال قيمة (Value Functions) أو سياسات (Policies).
•آلية التجربة والخطأ بدون برمجة صريحة لكل حالة.هذا الدمج حسّن إمكانيات الوكلاء في:
•التعميم عبر حالات جديدة لم تُشاهد أثناء التدريب.
•التعامل مع بيانات حسية غير مهيكلة دون هندسة خصائص يدوية.
•التكيف الذاتي في بيئات غير متوقعة.
1.3 أهمية DRL في الروبوتات
1.المرونة التشغيلية: تعلّم الروبوتات استراتيجيات جديدة دون تدخل بشري مستمر.
2.خفض التكلفة والصيانة: تقليل الحاجة لإعادة برمجة متكررة عند تغير بيئة العمل.
3.السلامة والأمان: تحسين رصد المخاطر وتجاوز العقبات في الزمن الحقيقي.
4. التطبيقات المتقدمة: من الأتمتة الصناعية إلى الخدمات اللوجستية والاستجابة للكوارث.
المراجع

التعلم العميق في الذكاء الاصطناعي: المفهوم، التطبيقات، والمزايا
استكشف عالم التعلم العميق في الذكاء الاصطناعي، حيث نناقش المفهوم الأساسي، أهميته، استخداماته المتنوعة، وآلية عمله
تصفح المرجع2. آلية عمل Deep RL: المكونات والتقنيات الأساسية
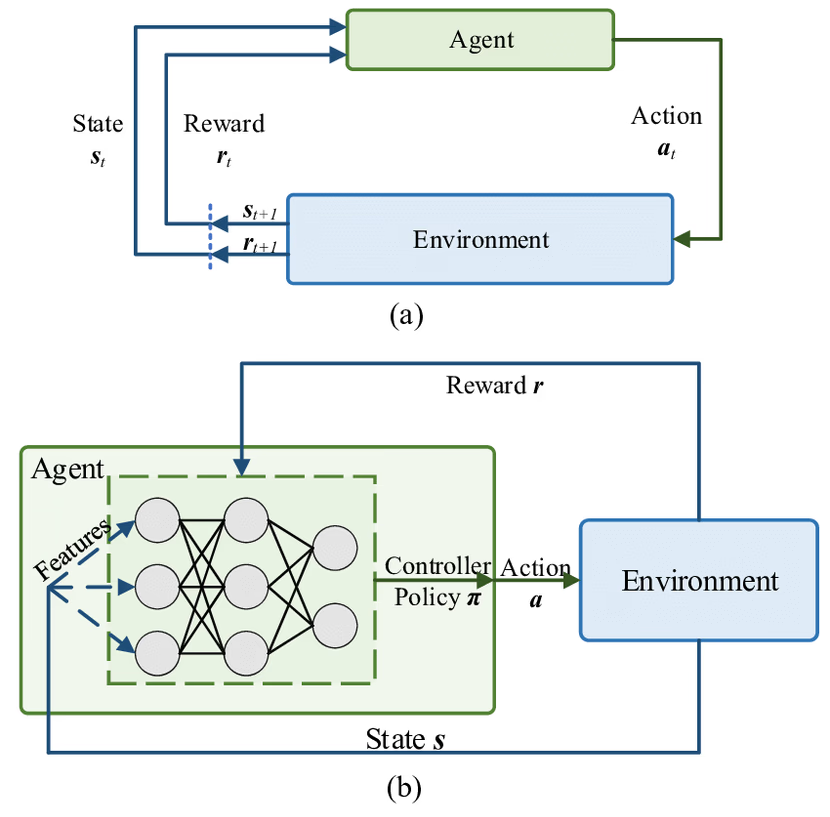
2.1 المكونات الرئيسية
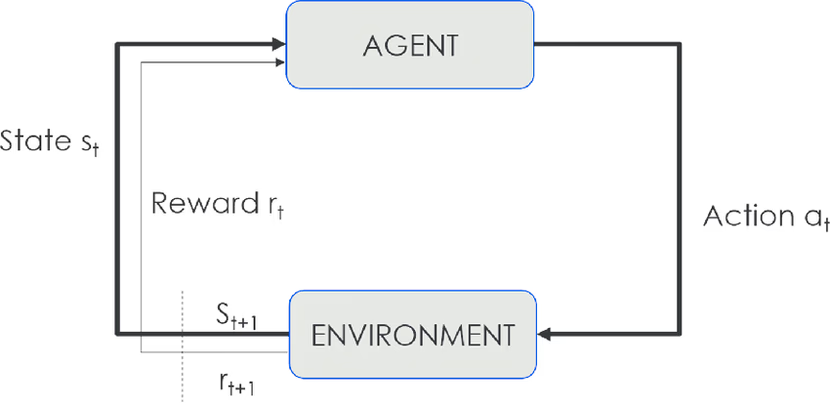
2.2 دورة التعلم التفصيلية
- الملاحظة (s): يستقبل الوكيل حالة مبدئية من البيئة.
- الإجراء (a): يختار الوكيل إجراءً وفق سياسته
- π(s).المكافأة (r): يحصل الوكيل على مكافأة فورية بناءً على جودة الإجراء.
- الانتقال (s′): تنتقل الحالة إلى الحالة الجديدة.
- التحديث (Update): يُحدّث الوكيل سياسته أو دوال القيمة عبر خوارزمية التعلم.
- التكرار: تستمر الدورة حتى تحقيق هدف أو انتهاء التجربة.
2.3 المعادلات والتقنيات الداعمة•
- معادلة بيلمان (Bellman Equation):•Q(s, a) ← E [ r + γ · max_{a′} Q(s′, a′) ]oγ: معامل الخصم (0 ≤ γ ≤ 1) يوازن بين المكافآت الفورية والمستقبلية.
- Experience Replay Buffer:تخزين التجارب (s, a, r, s′) وإعادة تشغيلها عشوائيًا لكسر ارتباط البيانات وتحسين استقرار التدريب.
- Target Networks:استخدام شبكة منفصلة لتقدير القيمة الهدفية تقلل التقلبات في تحديثات DQN.
•Normalization & Scaling:ضبط مدخلات الشبكة العصبية لتسريع التقارب وتحسين الاستقرار
المراجع

How is $Q(s', a')$ calculated in SARSA and Q-Learning?
I have a question about how to update the Q-function in Q-learning and SARSA. Here (What are the differences between SARSA and Q-learning?) the following updating formulas are given: Q-Learning $$Q...
تصفح المرجع3. أبرز خوارزميات DRL وتطورها (2023–2025)
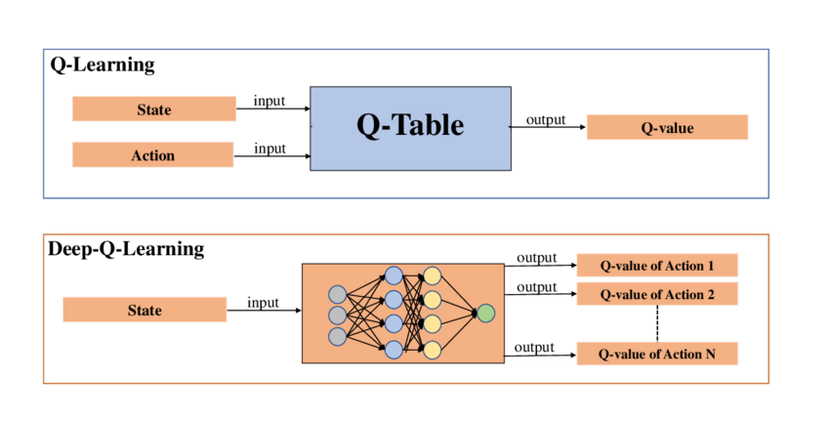
3.1 DQN (Deep Q-Network)
•الابتكار الأساسي: تقريب Q(s, a) بشبكة عصبية تلافيفية.
•التحسينات:
Double DQN: فصل اختيار الإجراء عن تقييمه لتقليل التحيز.
Prioritized Experience Replay (PER): اختيار الخبرات ذات أهمية أكبر أولًا.
Distributional RL & Rainbow: دمج عدة تحسينات (Double DQN، PER، Categorical DQN، N-step Targets) في إطار موحد.
•التحديات: استقرار التدريب وضبط المعلمات التجريبية.
3.2 PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization)
•المبدأ: تحسين السياسات باستخدام Clipped Surrogate Objective يقيّد حجم التحديث.
•الميزات:استقرار أعلى من خوارزميات Policy Gradient التقليدية.
قابليته للتوسع والتحكم في فضاءات إجراءات مستمرة.
•التطبيقات: تحريك روبوتات رباعية الأرجل وتحكم ذراع صناعي في محاكيات MuJoCo وGazebo.
3.3 SAC (Soft Actor-Critic)
•الابتكار: دمج إطار أقصى الإنتروبيا (Max Entropy) لتعزيز الاستكشاف العشوائي.
•المزايا:كفاءة عينات عالية: تقليل عدد الحلقات التدريبية المطلوبة.
استقرار تدريبي محسن: تجنب التقلبات الحادة.
•الاستخدام الصناعي: تخفيض استهلاك الطاقة في ذراع روبوت صناعي حتى %22.7 واستخدامه في تجنب العوائق للطائرات بدون طيار.
3.4 خوارزميات أخرى صاعدة
•Curiosity-Driven Exploration: يقدم مكافآت داخلية تشجع الوكيل على استكشاف حالات غير مألوفة.
•Model-Based RL: بناء نموذج ديناميكيات البيئة داخليًا لتقليل الحاجة للتفاعل المباشر وللتخطيط المستقبلي.
المراجع

How Are Neural Networks Used in Deep Q-Learning? - GeeksforGeeks
Your All-in-One Learning Portal: GeeksforGeeks is a comprehensive educational platform that empowers learners across domains-spanning computer science and programming, school education, upskilling, commerce, software tools, competitive exams, and more.
تصفح المرجع
What is Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO)? | Activeloop Glossary
Discover Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO), a reinforcement learning algorithm that efficiently solves complex tasks with real-world applications.
تصفح المرجع4. تطبيقات عملية: Boston Dynamics وغيرها
4.1 روبوت Atlas
•التحديات: الملاحة على تضاريس غير ثابتة، والحفاظ على التوازن أثناء قفزات ومعوقات.
•الحلول التقنية:
PPO + Model Predictive Control (MPC) للتخطيط اللحظي.oما يصل إلى 150 مليون محاكاة جمع بيانات واسعة.
•النتائج:
Zero-Shot Transfer: انتقال السياسات المستقاة من المحاكاة مباشرةً إلى الواقع دون تعديل.oتنفيذ مناورات باركور مع مقاومة اضطرابات خارجية.
4.2 روبوت Spot
•التقنية: Meta-RL لتكيّف سريع مع مهام جديدة عبر تعلم “كيفية التعلم”.
•استراتيجيات التدريب:oDomain Randomization لضمان عمومية السياسات عبر تغير خصائص المحاكاة (احتكاك، وزن، إضاءة).
استخدام فيديوهات VR من منظور الشخص الأول لتعليم مهارات الاسترداد والتلاعب.
•الأداء: نجاح يتجاوز 98% في استرداد الأشياء مقابل 73% للطرق التقليدية.
4.3 أمثلة صناعية أخرى
•أمازون وويرهاوس روبوتات: استخدام DRL لتحسين مسارات نقل الطرود تلقائيًا.
•ذراع KUKA الصناعية: تطبيق SAC وModel-Based RL لتحسين دقة الالتقاط والوضع وتقليل استهلاك الطاقة.•طائرات بدون طيار (UAVs): التركيز على تجنب العوائق والتنسيق متعدد الوكلاء في عمليات التفتيش والصيانة.
المراجع

Learning to Run (and Crawl): Inside Boston Dynamics’ Atlas Reinforcement Learning Demo | CTCO
A deep dive into the latest Boston Dynamics Atlas demo powered by reinforcement learning – covering its RL architecture, physics simulation, zero-shot sim-to-real transfer, human motion retargeting, and the massive scale (150M+ simulations) behind it. Includes parallels to generative AI and leadership takeaways on fostering innovation, simulation investment, AI-based control, and the future of work with robotics.
تصفح المرجع5. التحديات التقنية والحلول
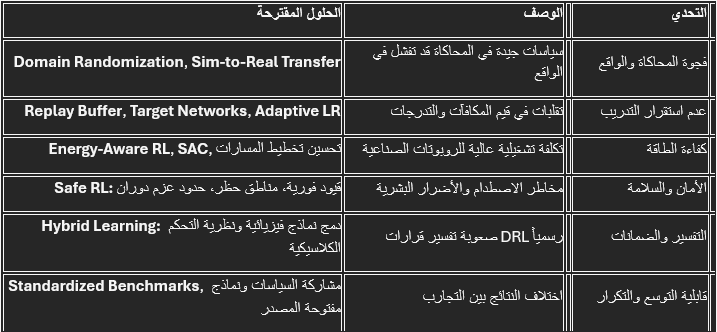
المراجع
Sim-to-Real Transfer of Robotic Control with Dynamics Randomization
Simulations are attractive environments for training agents as they provide an abundant source of data and alleviate certain safety concerns during the training process. But the behaviours developed by agents in simulation are often specific to the characteristics of the simulator. Due to modeling error, strategies that are successful in simulation may not transfer to their real world counterparts. In this paper, we demonstrate a simple method to bridge this "reality gap". By randomizing the dynamics of the simulator during training, we are able to develop policies that are capable of adapting to very different dynamics, including ones that differ significantly from the dynamics on which the policies were trained. This adaptivity enables the policies to generalize to the dynamics of the real world without any training on the physical system. Our approach is demonstrated on an object pushing task using a robotic arm. Despite being trained exclusively in simulation, our policies are able to maintain a similar level of performance when deployed on a real robot, reliably moving an object to a desired location from random initial configurations. We explore the impact of various design decisions and show that the resulting policies are robust to significant calibration error.
تصفح المرجع
Frontiers | A human-centered safe robot reinforcement learning framework with interactive behaviors
Deployment of Reinforcement Learning (RL) algorithms for robotics applications in the real world requires ensuring the safety of the robot and its environmen...
تصفح المرجع6. التوجهات المستقبلية (2025–2030)
1.التعلم الهجين (Hybrid RL–Control):
دمج DRL مع نماذج ديناميكية فيزيائية (ديناميكا لاجرانج، نظرية التحكم) لتوفير تفسير ومنطق للقرارات وضمانات سلامة.
2.التكيف في الزمن الحقيقي (Real-Time & Continual Learning):
وكلاء قادرون على تحديث سياساتهم أثناء التشغيل باستخدام بيانات واردة جديدة محدودة دون إعادة تدريب شامل.
3.العقلية العالِمة (World Models):
بناء نموذج داخلي لديناميكيات البيئة يسمح بالتحقق والتخطيط دون تفاعل مباشر مستمر.
4.التعلم بالتقليد من البشر (Imitation & Offline RL):
استخدام فيديوهات VR وبيانات مشغلين بشريين لتعلم مهارات معقدة، وتقليل الحاجة لهندسة مكافآت دقيقة.
5.التنسيق متعدد الوكلاء (Multi-Agent Systems):
تطوير استراتيجيات تواصل وتنسيق بين عدة روبوتات لأداء مهام مشتركة معقدة مثل فرق البحث والإنقاذ.
6.التنظيم والأخلاقيات:
وضع أطر تنظيمية تضمن سلامة وخصوصية استخدام روبوتات DRL في البيئات العامة والحساسة.
7.الاندماج مع البنى التحتية المستقبلية:
استخدام شبكات 5G/6G لأتمتة التعاون بين روبوتات متفرقة جغرافيًا وتبادل البيانات لحظيًا.
المراجع
Structure in Deep Reinforcement Learning: A Survey and Open Problems
Reinforcement Learning (RL), bolstered by the expressive capabilities of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) for function approximation, has demonstrated considerable success in numerous applications. However, its practicality in addressing various real-world scenarios, characterized by diverse and unpredictable dynamics, noisy signals, and large state and action spaces, remains limited. This limitation stems from poor data efficiency, limited generalization capabilities, a lack of safety guarantees, and the absence of interpretability, among other factors. To overcome these challenges and improve performance across these crucial metrics, one promising avenue is to incorporate additional structural information about the problem into the RL learning process. Various sub-fields of RL have proposed methods for incorporating such inductive biases. We amalgamate these diverse methodologies under a unified framework, shedding light on the role of structure in the learning problem, and classify these methods into distinct patterns of incorporating structure. By leveraging this comprehensive framework, we provide valuable insights into the challenges of structured RL and lay the groundwork for a design pattern perspective on RL research. This novel perspective paves the way for future advancements and aids in developing more effective and efficient RL algorithms that can potentially handle real-world scenarios better.
تصفح المرجعالخاتمة
يمثل التعلم التعزيزي العميق نقطة تحول في مجال الروبوتات الذكية، مقدّمًا نهجًا يدمج التعلم الذاتي مع قدرات التعميم في فضاءات ضخمة. من خوارزميات DQN وPPO وSAC التي حسّنت استقرار وكفاءة التدريب، إلى تطبيقات مبتكرة في روبوتات Boston Dynamics وAmazon وغيرهما، نلمس اليوم ثمار هذا البحث في تنفيذ مناورات معقدة، والتكيف السريع، وتحسين استهلاك الطاقة.ومع تزايد التحديات—فجوة المحاكاة والواقع، أمان البشر، تفسير القرارات—تلوح في الأفق حلول واعدة كالـDomain Randomization وSafe RL وHybrid Learning. وباتجاه 2030، نترقب انتشارًا أوسع للروبوتات المدعومة بـDRL في المصانع الذكية، والرعاية الصحية، واستكشاف الكوارث، وغيرها من المجالات الحيوية، لتكون شريكًا ذكيًا ومستدامًا في دفع عجلة الابتكار العالمي.